Non-Destructive test of cement is a technique to get the compressive strength and different properties of cement from the current designs. This test gives prompt outcomes and genuine strength and properties of substantial design.
The standard technique for assessing the nature of cement in structures or designs is to test examples cast at the same time for compressive, flexural and rigid qualities.
The principal drawbacks are that results are not gotten right away; that substantial in examples might contrast from that in the genuine design because of various relieving and compaction conditions; and that strength properties of a substantial example rely upon its size and shape.
In spite of the fact that there can be no immediate estimation of the strength properties of primary cement for the basic explanation that strength assurance includes damaging burdens, a few non-horrendous strategies for evaluation have been created.
These rest assured specific actual properties of cement can be connected with strength and can be estimated by non-disastrous strategies. Such properties incorporate hardness, protection from infiltration by shots, bounce back limit and capacity to communicate ultrasonic heartbeats and X-and Y-beams.
These non-horrendous strategies might be sorted as entrance tests, bounce back tests, take out methods, dynamic tests, radioactive tests, development idea. It is the motivation behind this Digest to depict these strategies momentarily, framing their benefits and burdens.
Techniques for Non-Destructive Testing of Concrete
Following are different methods of NDT on concrete:
- Penetration method
- Rebound hammer method
- Pull out test method
- Ultrasonic pulse velocity method
- Radioactive method
1. Penetration Method:
Limitations And Advantages
The test gives results variably and ought not be supposed to give precisely accurate values of strength of cement. It has, nonetheless, the potential for giving a speedy method for really looking at quality and development of in situ concrete.
2. Rebound Hammer Method :
The rebound back hammer is a surface hardness analyzer for which an exact relationship has been laid out among strength and rebound back number.
The main known instrument to utilize the rebound back standard for substantial testing is the Schmidt hammer, which weighs around 4 lb (1.8 kg) and is appropriate for both lab and field work. It comprises of a spring-controlled hammer mass that slides on an unclogger inside a rounded lodging.
The hammer is constrained against the outer layer of the concrete by the spring and the distance of bounce back is estimated on a scale. The test surface can be flat, vertical or at any point however the instrument should be aligned here.
Adjustment should be possible with chambers (6 by 12 in., 15 by 30 cm) of a similar concrete and total as will be utilized at work. The chambers are covered and immovably held in a pressure machine.
A few readings are taken, very much circulated and reproducible, the normal addressing the bounce back number for the chamber. This method is rehashed with a few chambers, after which compressive qualities are gotten.
Limitations and Advantages
The Schmidt hammer gives a cheap, straightforward and fast technique for getting a sign of substantial strength, however exactness of ±15 to ±20 percent is conceivable just for examples projected relieved and tried under conditions for which adjustment bends have been laid out.
The outcomes are impacted by variables, for example, perfection of surface, size and state of example, dampness state of the substantial, kind of concrete and coarse total, and degree of carbonation of surface.
3.Pull Out Test Method:
Limitations and Advantages
The pulse velocity technique is an optimal device for laying out whether cement is uniform. It tends to be utilized on both existing designs and those under development.
As a rule, in the event that huge contrasts in pulse velocity are found inside a design for reasons unknown, there is solid motivation to assume that damaged or decayed concrete is available.
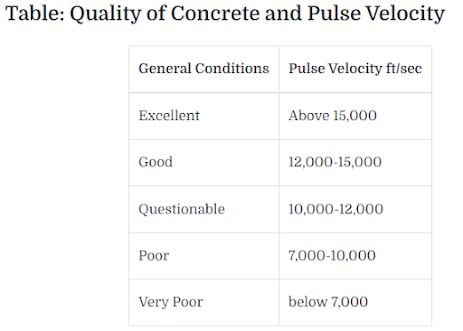
High pulse velocity readings are by and large characteristic of good quality cement. An overall connection between concrete quality and pulse velocity is given in Table.
Genuinely great connection can be gotten between solid shape compressive strength and pulse velocity. These relations empower the strength of underlying cement to be anticipated inside ±20 percent, gave the kinds of total and blend extents are steady.
The pulse velocity technique has been utilized to concentrate on the consequences for cement of freeze-defrost activity, sulfate assault, and acidic waters. By and large, the level of harm is connected with a decrease in beat speed. Breaks can likewise be recognized.
Extraordinary consideration ought to be worked out, in any case, in involving pulse velocity estimations for these reasons since interpreting results is frequently troublesome. Once in a while the pulse doesn't go through the harmed piece of the concrete.
The pulse velocity technique can likewise be utilized to appraise the pace of solidifying and strength improvement of cement in the beginning phases to decide when to eliminate formwork. Openings must be cut in the formwork so transducers can be in direct contact with the concrete surface.
As concrete ages, the pace of increment of pulse velocity dials back considerably more quickly than the pace of improvement of solidarity, so past a strength of 2,000 to 3,000 psi (13.6 to 20.4 MPa) exactness in deciding strength is under ±20%.
Exactness relies upon cautious adjustment and utilization of a similar substantial blend extents and total in the test tests utilized for alignment as in the construction.
In synopsis, ultrasonic pulse velocity tests have an extraordinary potential for concrete control, especially for laying out consistency and recognizing breaks or deformities. Its utilization for anticipating strength is significantly more restricted, attributable to the enormous number of factors influencing the connection among strength and pulse velocity.
5.Radioactive Method:
Radioactive techniques for testing cement can be utilized to recognize the area of support, measure thickness and maybe lay out whether honeycombing has happened in primary concrete units. Gamma radiography is progressively acknowledged in England and Europe.
The hardware is very basic and running expenses are little, albeit the underlying cost can be high. Concrete up to 18 in. (45 cm) thick can be analyzed easily.









.png)
3 Comments
https://engineeringeeks2011.blogspot.com/2022/07/non-destructive-test-of-cement.html
ReplyDeletesuch a valuable information
الف شكر لك
ReplyDeleteAre these tests really done on the site in or out
ReplyDelete