Fluid Mechanics Objective Questions (MCQ)
6. Which of the following is NOT a kind of force considered in the Navier-Stokes equation?
a) Gravity force
b) Pressure force
c) Surface tension force
d) Viscous force
Answer: c
Explanation: gravity, pressure force, and viscous forces together they constitute the derivation of the Navier-Stokes equation. Although the surface tension force acts on a moving fluid, it is considered negligible for the Navier-Stokes equation.
7. Fluid is said to be ideal?
a) non-viscous and incompressible
b) Viscous and compressible
c) Viscous and incompressible
d) incompressible
Answer: a
Explanation: Ideal fluids are fluids that have zero viscosity. This result in a flow called invisible flow. The invisible flow is non-viscous and incompressible since there is no shear force due to zero viscosity.
8. If a flow has the same parameters at any given point, then it is said
to be_________
a) Uniform flow
b) Quasi-static flow
c) Laminar flow
d) Static flow
Answer: d
Explanation: A flow that takes place at a constant speed without the change in cross section is called uniform flow. Its parameters remain constant at any given point.
9. Bernoulli's equation in fluid dynamics is valid for ____
a) Compressible flows
b) Temporary flows
c) Continuous flows
d) Viscous flows
Answer: c
Explanation: To answer this equation, we need to understand the assumptions utilized in Bernoulli's equation. Bernoulli's theorem is only valid for ideal, constant, in-compressible, continuous, invisible, and ir-rotational flows. So, out of the options, only continuous flows fit into the assumptions.
10. Water flows through a pipe at a speed of 2 m/s. The pressure gauge reading is 2 bars. The reference height is given in 2 m. Find the piezometric head.
(Assume all Bernoulli assumptions, Density of water = 1000 kg/m3, g = 9.8 m/s2).
a) 22.4m
b) 22.6m
c) 20.4m
d) 20.6m
Answer: a
Explanation:
The piezometric head is the addition of the pressure head
and the reference head.
The pressure head is given by
P / ρg = 20.4 m.
The reference height is 2 m,
which makes a total of 22.4 m.
The speed given is additional information.
11. A student wants to find the speed of air flowing through a pipe. He has a pressure gauge that shows only the dynamic pressure. The manometer reads 0.018 mm Hg.
Assume the density of air is 1.225 kg/m3,
find the velocity V of the air (ρg = 20.4 m, Hg = 13600 kg/m3).
a) 4 m/s
b) 2 m/s
c) 20 m/s
d) 40 m/s
Answer: b
Explanation: (0.018 mm Hg * 13.6 * 9.8) = 2.4 bar.
The dynamic pressure is given by ρg = 20.4 m.V 2 /2.
Equating 2.4 bar with dynamic pressure gives V = 2 m/s.
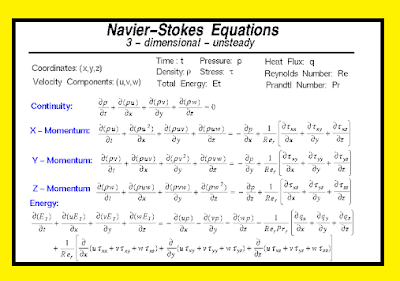
12. If the compressibility force and the surface tension force are neglected from Newton's second law of motion, which of the following equations results?
a) Navier-Stokes equation
b) Euler's equation
c) Bernoulli's equation
d) Reynolds equation
Answer: d
Explanation: Newton's second law of motion is made up of 6 forces, namely gravity, viscosity, pressure, turbulence, surface tension and compressibility forces. The Reynolds equation is made up of 4 forces. The surface tension force and the compressibility forces are neglected to find the Reynolds equation.
13. What does a Pitot tube measure? On what principle does a Pitot tube work?
a) Pressure, Bernoulli's principle
b) Velocity, Bernoulli's principle
c) Pressure, Euler equation
d) Velocity, Euler's equation
Answer: a
Explanation: Although a Pitot tube can be used primarily to find the velocity of a fluid, the Pitot tube measures pressure and not velocity. The Pitot tube works according to Bernoulli's principle since it gives us pressure.





.png)
3 Comments
2 much information
ReplyDeletePost new MCQ articles
ReplyDeletehttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6Xl0OWeImto&list=PLOEl8jQJfup10-NHdn0CV57Cddw6bSC0n&index=1&t=8s
ReplyDelete